C++ is a powerful, high-level programming language used for building software, applications, and systems. It is an extension of the C programming language and supports multiple programming styles such as procedural, object-oriented, and generic programming. C++ was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in the early 1980s at Bell Labs.
Table of Contents
Definition
C++ is an object-orient programming language that many observe as the best language for making large-scale submissions.
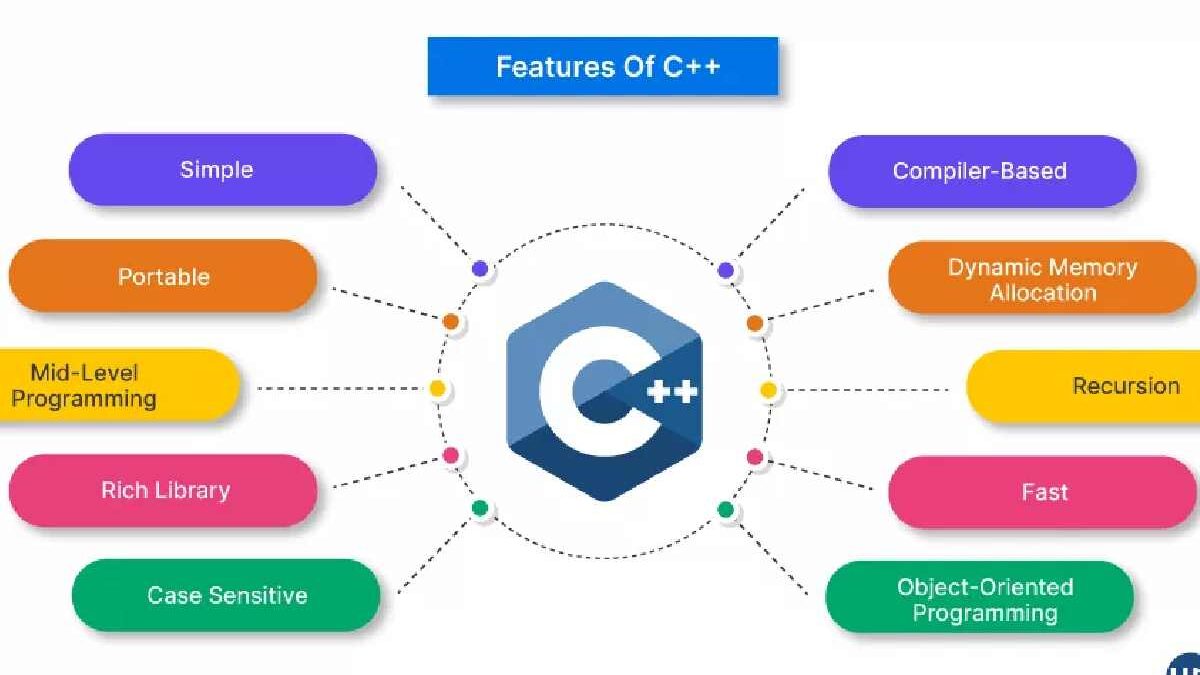
Key Features of C++
| Feature | Description | Why It Matters |
| Object-Oriented Programming | Supports classes and objects | Helps organize and reuse code |
| Low-Level Memory Access | Direct memory manipulation | Improves performance |
| Portability | Works across platforms | Code can run on different systems |
| Standard Template Library (STL) | Built-in data structures & algorithms | Faster development |
| Multi-Paradigm Support | Procedural + OOP + Generic programming | Flexible coding approach |
| Fast Execution | Compiled language | Ideal for high-performance applications |
How C++ Works?
C++ is a compiled language. This means:
- You write the source code.
- A compiler translates it into machine code.
- The computer executes the compiled program.
Because it compiles directly into machine-level instructions, C++ programs are extremely fast.
What are the Uses of C++?
C++ is used in many ways to capitalize on its flexibility and performance. Some of the primary uses
Operating systems
C++’s low-level capabilities allow for efficient memory management and system resource controls, making it well-suited for
Games and graphics.
C++’s high performance and ability to interact with hardware makes it a good choice for game engines such as Epic Games’ Unreal Engine and Unity Technologies’ Unity, built using C++. The programming language is also used for graphics programming tasks like real-time rendering, image processing, and physics simulations.
Embedded systems
C++ is commonly used to develop embedded systems, computer systems designs to perform specific tasks. Examples of embedded systems include medical devices, automotive systems, and Internet of Things devices.
Software libraries
C++ serves as the foundation for many high-level libraries used in various domains. Libraries like Boost provide additional functionality and utilities for C++ programmers, while the Standard Template Library (STL) offers a collection of generic data structures and algorithms. These libraries provide ready-to-use components, enhancing developer productivity.
High-performance computing (HPC).
C++ is well-suite for HPC applications that require maximum computational efficiency and parallel processing. It’s used in scientific simulations, numerical analysis, mathematical modeling, and simulations of physical phenomena. It’s frequently used alongside specialize libraries, such as the message-passing interface and Open MP for distribute and parallel computing.
Web development
Although C++ isn’t commonly used for web development, it plays a crucial role in the back end of web applications, such as web servers, network protocols, routers, and communication software. Many web frameworks and servers, including the Apache HTTP Server, are implemented in C++. The language’s speed and reliability make it suitable for handling high-traffic websites and complex server-side operations.
Systems programming
C++ is often used for systems programming tasks, where interaction with the underlying hardware and OS is required. Software like device drivers, network protocols, and system utilities are typically implementing .
Applications of C++
C++ is widely used across industries because of its speed, efficiency, and system-level capabilities. Below is a table showing the major applications of C++ along with examples.
| Application Area | Description | Examples / Companies |
| Operating Systems | Used to develop core system software due to high performance and hardware control. | Microsoft Windows, Linux |
| Game Development | Popular for building high-performance game engines and graphics-heavy games. | Epic Games (Unreal Engine), Ubisoft |
| Embedded Systems | Used in devices like cars, medical equipment, and smart appliances. | Automotive systems, IoT devices |
| Web Browsers | Helps in developing fast and secure browser engines. | Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox |
| Database Systems | Used to manage large amounts of data efficiently. | Oracle, MySQL |
| Financial and Banking Systems | Supports high-speed trading, transaction processing, and security. | Stock exchanges, fintech companies |
| Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning | Used for performance-intensive AI algorithms and frameworks. | Robotics, computer vision systems |
| Robotics and Automation | Controls robots and automated industrial systems. | Manufacturing robots |
| Cloud and Distributed Systems | Used to build scalable and reliable backend systems. | Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure |
| Scientific and Engineering Applications | Used for simulations, research, and high-performance computing. | Space, defense, and research institutions |
How to Install C++ (Step-by-Step Guide)
To start coding in C++, you need a compiler and a code editor or IDE. The process depends on your operating system such as Windows, Linux, or macOS. Below is a simple guide.
Installing C++ on Windows
1: Download a Compiler
The most common option is MinGW (Minimalist GNU for Windows).
Go to the official MinGW website
Download and install the GCC (GNU Compiler Collection).
GCC is maintained by GNU Project and is widely used.
2: Install MinGW
- Run the installer.
- Select C++ compiler (g++).
- Complete installation.
3: Set Environment Variables
- Open System Properties → Advanced → Environment Variables.
- Edit Path and add the MinGW “bin” folder.
- Click OK.
4: Install a Code Editor or IDE
You can use:
- Visual Studio Code
- Code::Blocks
- Dev-C++
- Visual Studio
These help you write and run C++ programs easily.
5: Verify Installation
- Open Command Prompt.
- Type:
- g++ –version
- If the version appears, C++ is installed successfully.
Installing C++ on Linux
Most Linux systems already have GCC.
Steps:
- Open Terminal.
- Run:
- sudo apt update
- sudo apt install g++
- Verify:
- g++ –version
Installing C++ on macOS
Steps:
- Install Xcode Command Line Tools:
- xcode-select –install
- This includes the GCC compiler.
- Verify:
- g++ –version
Advantages and Disadvantages
C++ comes with a mix of advantages and disadvantages. Some of its benefits, such as high performance and control, come with the challenge of complexity
and steep learning curves.
Advantages of C++
| Advantage | Explanation |
| High Performance | Suitable for game engines and system software |
| Memory Control | Developers can manage RAM efficiently |
| Large Community | Strong developer support |
| Industry Standard | Used in major software products |
| Scalable | Suitable for both small and large applications |
The advantages of C++ are
1. High performance
2. Control
3. Flexibility
4. Software portability
5. Compatibility
6. A spacious ecosystem
High performance
- low-level memory operation and direct access to hardware make it suitable for resource-intensive applications.
- Control
- It controls system resources and enables developers to fine-tune their programs for optimal performance.
Flexibility
- It results in functionality such as the support of OOP and procedural and functional programming, which is increasingly involve at enterprise scale.
Software portability
- It lets programs run on several different platforms.
Compatibility
- It enables interoperability with other programming languages, such as C, and also its support across different platforms. This lets developers reuse code and use third-party libraries.
A spacious ecosystem
- It provides the ability to use a wide selection of collections and also a frameworks that offer prebuilt approaches for tasks, such as data manipulation, which reduces the need for manual execution.
Disadvantages of C++ are
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
| Complex Syntax | Harder for beginners |
| Manual Memory Management | Risk of memory leaks |
| Steep Learning Curve | Requires deeper understanding |
1. Complexity
2. Security risks
3. Manual memory management in
4. Lack of built-in garbage collection
5. Complex syntax in
6. Long compile time
Complexity
C++ knowledge curve is challenging for beginners because of its extensive feature set.
Manual memory management
This may lead to memory waste and other memory management issues
Security risks
This is related to direct access to memory, which increases the risk of writing insecure code.
Lack of built-in garbage collection
Therefore it forces the developers to deallocate memory when it’s no longer need.
Complex syntax
Thus, code reading and writing consume more time than other programming languages.
Long compile time in
Therefore it may take more time compared to languages with dynamic typing.
Examples of C++ Usage with Company
Many global technology companies use C++ for building high-performance and scalable software. Below is a table showing real-world examples of how C++ is applied in different industries.
India
| Company Name | Industry | How C++ Is Used | Example Applications |
| Tata Consultancy Services | IT Services & Consulting | Developing system software, embedded solutions, and enterprise applications. | Banking software, telecom systems |
| Infosys | IT & Software | High-performance backend systems, financial and automation software. | Core banking, trading platforms |
| Wipro | IT & Digital Services | Embedded systems, cybersecurity, and enterprise software. | Automotive and IoT applications |
| HCL Technologies | Technology & Engineering | Operating systems, cloud, and system programming. | Networking and infrastructure tools |
| Tech Mahindra | Telecom & IT | Telecom network software and real-time communication systems. | 5G and telecom solutions |
| Paytm | Fintech & Payments | Secure, high-speed transaction systems and backend processing. | Payment gateways, fraud detection |
| Zerodha | Financial Technology | Trading platforms requiring speed and performance. | Stock trading and algorithmic trading |
| ISRO | Space & Research | Simulation, satellite control, and embedded systems. | Rocket and satellite software |
| DRDO | Defense & Research | Real-time systems, defense simulations, and automation. | Missile and radar systems |
| Bosch India | Automotive & Engineering | Embedded automotive software and smart systems. | Vehicle control and automation |
UK
| Company (UK) | Industry | How C++ Is Used | Example Products / Services |
| ARM Holdings | Semiconductor & Embedded Systems | Development of processor architectures, firmware, and embedded software. | ARM chips used in smartphones and IoT devices |
| BT Group | Telecommunications | Network systems, performance optimization, and infrastructure software. | Broadband and communication services |
| Rolls-Royce Holdings | Aerospace & Engineering | Real-time systems, simulation, and control software. | Aircraft engine monitoring and automation |
| Barclays | Banking & Finance | High-frequency trading, risk analysis, and financial modeling. | Trading platforms and banking systems |
| HSBC | Banking & Financial Services | Secure transaction systems and data processing. | Global banking and financial services |
| BAE Systems | Defense & Security | Embedded software and simulation for defense systems. | Military and cybersecurity solutions |
| Imagination Technologies | Graphics & AI | GPU development and multimedia processing. | PowerVR graphics technology |
| Ocado | E-commerce & Robotics | Automation, robotics, and logistics systems. | Warehouse automation platforms |
| Dyson | Consumer Technology | Embedded systems and product software. | Smart home and appliance control |
| Darktrace | Cybersecurity & AI | High-performance analytics and threat detection systems. | AI-based cybersecurity platforms |
USA
| Company Name | Industry | How C++ Is Used | Example Applications |
| Microsoft | Software & Cloud | System programming, OS development, performance tools | Windows components, game engines |
| Internet & AI | Backend systems, browser engines, AI frameworks | Chrome browser engine, search infrastructure | |
| Meta Platforms | Social Media & VR | High-performance backend systems and AR/VR development | Social media infrastructure, VR systems |
| Amazon | E-commerce & Cloud | Cloud infrastructure and large-scale distributed systems | AWS services, backend systems |
| Apple | Consumer Electronics | Operating systems, graphics engines | macOS components, device software |
| Tesla | Automotive & AI | Embedded systems, autonomous driving software | Vehicle control systems |
| NVIDIA | Semiconductor & AI | GPU drivers, AI frameworks, graphics processing | Graphics engines, CUDA platform |
| Adobe | Software & Media | Graphics rendering engines and performance tools | Photoshop and media software components |
| Oracle | Database & Enterprise | Database engines and enterprise systems | Database management systems |
| Epic Games | Gaming | Game engine development | Unreal Engine |
Conclusion
In the above article, we have discussed some essential points. We hope that you find the above content informative and helpful. To read more informative articles, keep visiting our website.