A Record Information Management (RIM) program is a system for managing records throughout their lifespan, stretching from their initial creation to their eventual destruction everywhere.
Table of Contents
What is Records Information Management?
Records Information Management (RIM) refers to the systematic control of records throughout their lifecycle — from creation and active use to storage, archiving, and final disposal. It ensures that organizational data is secure, accessible, compliant with regulations, and properly maintained.
RIM applies to both physical records (paper files, contracts) and digital records (emails, PDFs, databases, cloud documents).
Objectives of Records Information Management
| Objective | Description | Business Impact |
| Data Organization | Structured storage of records | Faster retrieval |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting legal retention requirements | Avoid penalties |
| Risk Reduction | Protecting sensitive information | Prevent breaches |
| Cost Optimization | Reducing unnecessary storage | Lower operational costs |
| Efficiency | Streamlining workflows | Improved productivity |
Why RIM Is Important
RIM plans help businesses improve records management in several ways, including:
They are implementing well-organized and active information to support and update everyday workflow.
We are enabling and maintaining record organization of legal requirements and obedience.
They ensured records storage, management, and disposal to protect sensitive documents.
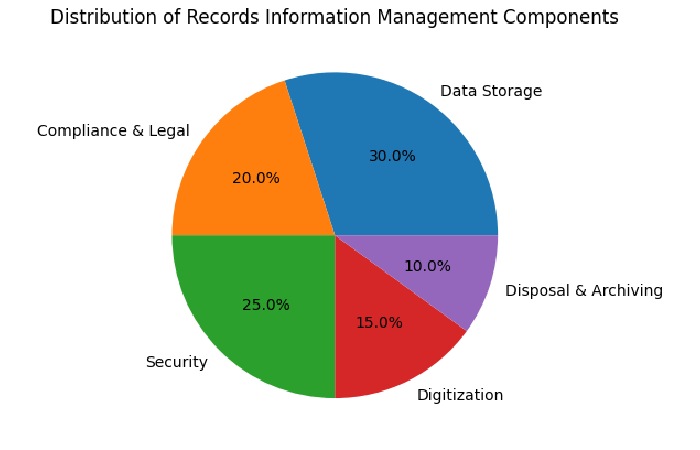
Key Components of Records Information Management
| Component | Function | Importance Level |
| Data Storage | Physical or digital storage systems | High |
| Compliance & Legal | Regulatory adherence | High |
| Security | Data protection and access control | Critical |
| Digitization | Converting paper to digital format | Medium |
| Disposal & Archiving | Secure retention and destruction | Medium |
How to Store & Manage Records
There are two primary choices for records storage and administration—hard-copy storage or digital files with electronic administration systems. It would be best to consider your business’s needs for the best design.
When you need to keep records you hardly use, packing the hard copies off-site will be cheaper than scanning them while freeing up the space in a paperless office.
On the flip side, when files are regularly used and distributed, using an electronic management document system helps save on supply costs like paper and printer ink and opens up old storage space for more productive purposes.
In some cases, when files are outdated or unused, they can be immediately disposed of. However, some records are legally required to be stored and managed.
Best Practices for Effective Records Information Management
| Practice | Implementation Strategy |
| Develop Retention Policy | Define timelines for record storage |
| Use Digital Solutions | Implement document management systems |
| Access Control | Role-based permissions |
| Regular Audits | Periodic compliance checks |
| Employee Training | Educate staff on data handling |
Benefits
1. Control the Generation and Growth of Records
Even though we are increasing electronic files, the amount of paper used in offices has not significantly reduced. If a record is accepted, a group can control the creation of records or duplicates and hold only needed or active ones. This contains the growth of documents and thus reduces the storage space required.
2. Effectively Retrieve and Dispose Records
The penalties for spending too much time searching for misfiled records may cause loss not only of billable hours but also valuable customers. This is why investing in a well-designed filing system that can facilitate recovering documents and arranging papers past their end-of-life date is essential.
3. Assimilate New Records Management Technologies
Investing in record management software can be helpful if a company has a physical record management system. The new record management technology can be adapted to the existing records system to make the system more robust.
4. Regulatory Compliance
When the government toughens compliance issues, companies must apply a sound record organization system and ensure complete submission to laws and regulations. If any company fails to provide vital records during litigation or regulatory checks, it may have to pay severe penalties or face legal significance. The only way to ensure regulatory compliance is through advanced record management technology and a firm policy for records management and preservation.
5. Minimize Litigation Risks
It can reduce the risk of process and possible prices. A well-planned and thoughtfully applied record management program can reduce the liabilities associated with document removal.
6. Safeguard Important Information
Public or private companies need an organized program to protect their vital records and information from tragedy or theft. It conserves the integrity and confidentiality of important documents and safeguards them per set rules. It stops illegal users from interfering with sensitive and essential records.
7. Cut Costs, Save Time & Efforts
To maintain an organized record system, conducting Records takes up much time and money for storage space, printing, filing, and staffing. Searching or duplicating lost records without an organized system also takes time and money. This system can help save significant expenses by falling operating costs and improving the efficiency of employees.
8. Better Management Decision Making
Making applicable data easily allows companies to make conclusions faster to stay ahead of the competition or create up-to-date decisions. It also makes valuable data accessible and disposes unwanted data; relevant data can be accessed faster. Indexing and recovery skill allows managers and lawful executives to search and find files more quickly.
9. Preserve Company Knowledge
A company’s files are its knowledge base, integral to its future planning and decision-making. Every record created in a business day is possible background data for future management decisions and planning. These records text the company’s activities, which managers may use to research the company’s workings.
10. Keep Employees Motivated
Poorly managed records, a messy splinter system, and everyday loss of essential documents create a poor working environment, directly affecting employee motivation. Though you cannot quantify the loss of inspiration due to these conditions, it is one of the most significant reasons to begin a sound record management system.
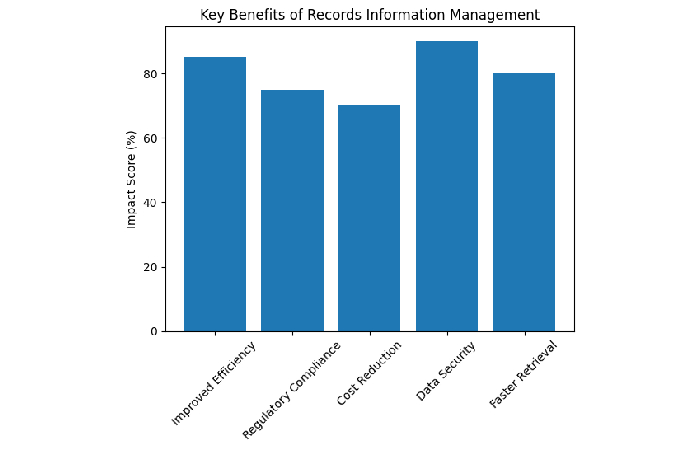
Benefits of Records Information Management
| Benefit | Description | Impact Score (%) |
| Improved Efficiency | Quick retrieval of records | 85% |
| Regulatory Compliance | Avoid legal penalties | 75% |
| Cost Reduction | Minimize storage expenses | 70% |
| Data Security | Prevent unauthorized access | 90% |
| Faster Retrieval | Reduced search time | 80% |
Types of Records Information Management
| Type of RIM | Description | Examples |
| Physical Records Management | Managing paper-based and hard-copy documents stored in files or archives. | Contracts, printed reports, legal files |
| Electronic Records Management (ERM) | Managing digital records such as emails, databases, and electronic documents. | PDFs, spreadsheets, digital forms |
| Cloud Records Management | Storing and managing records using cloud platforms for remote access and scalability. | Cloud storage, SaaS data |
| Legal and Compliance Records Management | Ensuring records meet legal, regulatory, and audit requirements. | Tax records, compliance documents |
| Financial Records Management | Handling financial documents for audits and reporting. | Invoices, payroll, budgets |
| Healthcare Records Management | Managing patient and medical records securely. | Medical histories, prescriptions |
| Human Resource Records Management | Maintaining employee-related records. | Recruitment, performance, training |
| Administrative Records Management | Managing operational and organizational documents. | Policies, meeting minutes |
| Archival Records Management | Preserving important historical or long-term records. | Corporate history, research data |
| Data Lifecycle Management | Managing records from creation to disposal. | Retention schedules, deletion policies |
Challenges in Records Information Management
The Information Management Records Information Management (RIM) has a number of challenges that are critical in the current data-driven environment. The large volume of digital data that increases at an alarming rate is one of the major problems, and storage and classification as well as retrieval become more complex. Another challenge is to ensure the data security and adherence to the regulations, particularly with the changing privacy regulations.
Poor record-keeping and non-standardized retention policies are also the bane of organizations. The process of modernizing the legacy systems through the integration of modern technologies may cause inefficiency and data silos. Moreover, lack of employee training and awareness on records management policies usually results in mistakes, duplication and legal risks, which affect the general efficiency of operations and decision mechanisms.
Challenges in Records Information Management
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
| Data Overload | Storage costs increase | Data classification |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Data breach risk | Encryption |
| Regulatory Changes | Compliance confusion | Legal updates |
| Poor Organization | Retrieval delays | Indexing systems |
Examples of Records Information Management (RIM)
Many organizations in India use Records Information Management (RIM) to manage data securely, maintain compliance, and improve operational efficiency. Below are real-world examples.
INDIA
| Company Name | Industry | How RIM Is Used | Example Records Managed |
| Tata Consultancy Services | IT & Consulting | Digital document management and secure client data storage. | Project files, contracts, client records |
| Infosys | IT Services | Electronic records and compliance management for global clients. | Financial data, HR and legal records |
| Wipro | Technology | Cloud-based records and cybersecurity solutions. | Customer data, IT system logs |
| HCL Technologies | Engineering & IT | Enterprise content and data lifecycle management. | Business documents, technical records |
| State Bank of India | Banking | Secure management of customer and financial records. | Loan files, KYC, transaction history |
| ICICI Bank | Banking & Finance | Compliance and digital document storage. | Account records, audit documents |
| Apollo Hospitals | Healthcare | Electronic medical record systems for patient care. | Patient history, prescriptions |
| Reliance Industries | Energy & Retail | Corporate governance and archival management. | Legal contracts, business reports |
| Flipkart | E-commerce | Customer data and transaction records. | Order data, digital invoices |
| Iron Mountain | Records Management | Physical and digital records storage services. | Archived files, compliance records |
London
| Company Name | Industry | How RIM Is Used | Example Records Managed |
| HSBC | Banking & Finance | Secure storage and management of financial and customer records. | Account details, transactions, compliance files |
| Barclays | Banking | Digital document and risk management for regulatory compliance. | Loan files, audit reports |
| Lloyds Banking Group | Financial Services | Customer data management and long-term archiving. | Customer profiles, financial statements |
| BP | Energy & Oil | Corporate governance and regulatory record keeping. | Contracts, safety and environmental records |
| Deloitte | Consulting & Audit | Compliance and client information management. | Audit documents, legal records |
| PwC | Consulting | Digital records and data governance for global clients. | Tax and financial documents |
| NHS | Healthcare | Electronic health records and patient data security. | Patient history, prescriptions |
| British Airways | Aviation | Operational and customer information management. | Booking data, employee records |
| Vodafone | Telecommunications | Customer and service data management. | Subscriber data, billing records |
| Iron Mountain | Records Management | Physical and digital storage, archiving, and compliance. | Archived corporate and legal files |
Europe
| Company Name | Country | Industry | How RIM Is Used | Example Records Managed |
| Siemens | Germany | Engineering & Technology | Digital document management and compliance for global projects. | Technical files, contracts |
| SAP | Germany | Software & IT | Enterprise data governance and digital record storage. | Client data, financial records |
| Deutsche Bank | Germany | Banking | Secure customer and financial record management. | Transaction history, audit files |
| Airbus | France | Aerospace | Long-term archival of engineering and safety records. | Design documents, compliance records |
| TotalEnergies | France | Energy | Regulatory and environmental documentation management. | Legal, safety, and environmental records |
| HSBC | UK | Financial Services | Customer data governance and compliance. | Account and loan records |
| Nestlé | Switzerland | Food & Beverage | Product and quality documentation for global operations. | Quality reports, supplier contracts |
| Philips | Netherlands | Healthcare & Technology | Patient data and regulatory record management. | Medical device and patient records |
| Vodafone | UK | Telecommunications | Subscriber and billing data management. | Customer and service data |
| Iron Mountain | Multiple | Records Management | Physical and digital archiving services across Europe. | Archived business records |
Records Information Management Jobs with Salary
| Job Role | Key Responsibilities | Average Salary in India (₹/year) | Average Salary in London (£/year) | Average Salary in Europe (€ /year) |
| Records Clerk | Organizes, files, and maintains physical & digital records | ₹2 – ₹4 lakh | £20,000 – £28,000 | €25,000 – €32,000 |
| Records Analyst | Reviews data, ensures compliance, manages documentation | ₹4 – ₹7 lakh | £30,000 – £40,000 | €35,000 – €45,000 |
| Records Manager | Oversees records lifecycle, policy creation, auditing | ₹7 – ₹15 lakh | £45,000 – £65,000 | €50,000 – €75,000 |
| Information Governance Officer | Ensures regulatory compliance and data security | ₹8 – ₹18 lakh | £50,000 – £70,000 | €55,000 – €80,000 |
| Document Controller | Controls document flow in industries like construction | ₹4 – ₹10 lakh | £30,000 – £50,000 | €35,000 – €55,000 |
| Compliance Specialist | Manages risk, legal and regulatory records | ₹10 – ₹20 lakh | £55,000 – £75,000 | €60,000 – €85,000 |
| Data Privacy Officer | Handles GDPR, data protection, and privacy records | ₹15 – ₹30 lakh | £70,000 – £100,000 | €80,000 – €120,000 |
| Digital Records Manager | Manages cloud, electronic and AI-driven records | ₹12 – ₹25 lakh | £65,000 – £95,000 | €75,000 – €110,000 |
Conclusion
In the above article, we have discussed some essential points related to Records information management. We hope that you found the above helpful content. To know more information about this article, keep visiting our website.

